The health benefits of cupping are becoming more mainstream amongst average people. Its benefits are not unknown, however, amongst celebrities such as Jennifer Aniston, David Arquette, Michael Phelps, and Gwyneth Paltrow who have all been seen sporting the recognizable cupping circle marks on their skin. Cupping, usually accompanied by acupuncture and other alternative therapies, helps with a variety of conditions, and has been practiced for many centuries. It was even mentioned as far back as 1,550 B.C. with the Egyptians using cupping in the Ebers Papyrus, one of the oldest medical textbooks in the world, and in 300 A.D. in China.
What is Cupping Therapy?
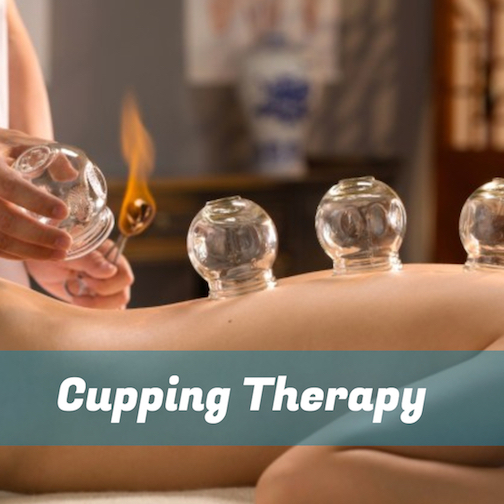
Cupping is an ancient modality used in the Middle East and China for thousands of years for poor energy flow, tight muscles, and to sedate the nervous system. It is often done in conjunction with acupuncture, but can also be a stand-alone treatment. The cups, historically made of clay or bamboo, are now made of either glass, silicone, or plastic. Cupping, with a physical mechanism involving suction, are usually placed on the back, but can be used for treatment on other places throughout the body such as the arms or thighs. There are many ways that an acupuncture provider can create suction. They can either use a flame to heat the inside of the cup (no worries, the flame does not go on your skin) or use rubber pumps to create suction.
Variations of cupping therapy:
- Quick Cupping – removing the cups quickly once the skin is vacuumed into the cup.
- Fixed Cupping – the cups are held in place at different variations of strength to treat the problematic area.
- Sliding Cupping – oil is applied to the area where the cups are to be placed which allows the practitioner to move the cups as needed over the skin. This allows them to see where there is poor blood flow. The darker the marks, the worse the circulation is.
- Cupping with Retention – leaving cups on for an extended time of 10 – 15 minutes.
- Fire Cupping – using usually either an alcohol-soaked cotton ball or herbs, the practitioner will light it placing it inside of the cup to burn up all of the oxygen inside the cup to create a vacuum. The cups will then be placed on the skin at strategic points creating a vacuum, and depending on the acupuncturist or alternative practitioner, they will either move the cups around using massage oil or leave the cups in place for an amount of time for your specific issue.
- Needle Cupping – done by acupuncturists, this variation is when the cups are placed over an acupuncture needle once it is inserted.
Types of Cupping:
- Dry Cupping – a noninvasive technique that uses
suction to increase the blood flow.
- Wet Cupping – the same as dry cupping, but takes it a step further by making small incisions to the cupped area to release a small amount of blood. Wet cupping needs to be performed in a sterile environment with sterile tools.
No matter which type of cupping is involved, it is important that you see a skilled practitioner who is trained in cupping, and using sterilized cups.
There are an infinite number of conditions/issues that cupping can be utilized for, and accompanying it with acupuncture only amplifies the results.
Conditions cupping could help with:
- Varicose veins
- Neck pain
- Back pain
- Herpes zoster
- High blood pressure
- Blood disorders
- Cellulite
- Eczema
- Acne
- Cholesterol (lowering it)
- Allergies
- Migraines & Headaches
- Fibromyalgia
- Fatigue
- Disc Herniation
- Bronchial Congestion
- Anxiety/Depression
- Digestive issues
- Rheumatic diseases
There are many conditions treated with cupping, and although the amount of research concerning cupping is small, the results are encouraging.
Cupping Benefits
The benefits of cupping may surprise you as there is still so much that most people do not know about it.
Cupping Benefits:
- Alleviate stress & emotional trauma – in the on-the-go world we live in, stress is a huge factor in many chronic health conditions including anxiety and depression, digestive disorders, and fatigue. Cupping relieves the physical tension that often accompanies heavy emotions and stress.
- Decreases congestion – in ancient times, cupping was used for conditions like pneumonia, bronchitis, and pulmonary tuberculosis. It still yields healing for alleviating chest congestion, clearing mucus from allergies, and suppressing coughs. The most common place on the body to have a cupping treatment, the upper back, benefits the lungs to release phlegm while making space for deeper breathing.
- Reduces pain – cupping is very helpful for pain related to the back, neck, shoulders, headaches, tight muscles, and sports injuries. While it seems too good to be sure, the science behind it says it all. In this systematic review from 2014, Cupping Therapy for Acute and Chronic Pain Management, concluding there to be positive effects on reducing pain intensity compared with heat therapy, conventional drugs, and no treatment at all.
- Improves the immune system – According to a study done in 2017, The Medical Perspective of Cupping Therapy, stating that “cupping seems to play a role in the activation of a complement system as well as modulation of a cellular part of the immune system.” Cupping benefits the immune system by launching “artificial local inflammation” which cues the body to deliver antibodies that clear damaged cells.
- Improves recovery time – cupping is known to aid in sports injuries, and can help speed up recovery time for optimum performance. It is also used by many athletes as a preventative for soreness, mobility, and loosening tight muscles.
Overall, if you are interested in cupping, make sure you speak with your acupuncture provider for an evaluation, and come up with your cupping and/or acupuncture treatment plan.
Cupping Treatment Information
In general, you will get anywhere from 3 – 5 cups for your first session, and rarely more than 5 – 7 cups thereafter according to the British Cupping Society. The cups are left on usually between 5 and 10 minutes with dry cupping, and only for a few minutes with wet cupping before the cup is removed to create a small incision. After your treatment, the treated areas get an ointment and bandages to prevent infection.
Side effects of cupping:
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
- Swelling
- Discolored circular marks on the skin
The infamous discolored marks left on the skin are a therapeutic and anticipated side effect, and usually in about a week to 10 days depending on the person. That being said, cupping is not the right treatment for everyone, and there are times when it should be avoided.
Scenarios/groups where cupping should be avoided:
- If you are sunburned
- Are on blood thinning medication
- Internal organ disorder
- Have a skin ulcer
- Have a wound (broken, irritated, or inflamed) where the cups will be placed
- Children under the age of four
- Seniors as their skin is more fragile
- Women who are pregnant for the abdomen and lower back
- Those on their menstruation cycle
While cupping is a safe treatment, it is important to take considerations when selecting a practitioner to perform your cupping therapy. For acupuncturists, cupping is usually a part of their curriculum in their education. Do not be afraid to ask questions, and do your research. Do you have a condition that may benefit from cupping? What method of cupping does the acupuncturist use? Is the facility clean? All of these things are good starting questions before booking a cupping treatment. It is also important to note that cupping is great for ongoing pain, but is not for a health emergency.
Cupping Treatment for You
Although cupping is in its earlier stages of research for various conditions, it shows great results and promise for future larger studies in its favor. It is safe, effective, and worth giving a try in the hands of a well-trained professional such as a licensed acupuncture provider. Speak with your acupuncturist to see if cupping is right for you.

Acupuncture Near Me
Get acupuncture near you today with Best Acupuncture Near Me, and contact a local acupuncture practitioner to find out if acupuncture is right for you.